Cloud migration is a major undertaking for any organization, and it is difficult to figure out the best cloud migration method that fits your business needs. To make cloud migration successful, it is essential to have an experienced team that understands cloud architecture and has deep knowledge of cloud technologies and platforms.
Understanding complexities of applications will help create an efficient cloud migration strategy and choose the right cloud migration method so that organizations can ensure their workloads are securely migrated with minimal downtime.
What is Cloud Transformation and Migration?
There is often a misconception between cloud transformation and migration.
Cloud transformation is about moving all data, apps, and storage. You need to reconfigure and optimize the entire business workloads/operations from onsite infrastructure to cloud servers.
Cloud migration is moving your business data and apps to cloud servers from on-premises servers. It is also a process of moving data from one cloud to another. For example, moving GCP to Azure. Therefore, every cloud migration is not cloud transformation, but every cloud transformation involves cloud migration.
Challenges of Cloud Migration
Cloud provides organizations with many benefits, including increased agility, lower costs, and improved scalability. However, migrating workloads to cloud can be challenging. Common challenges include:
- Lack of resources: Migrating to the cloud requires significant resources, including technical expertise and manpower. Organizations may not have the necessary resources internally and may need to seek external help.
- Complexity: Legacy applications can be complex, making it difficult to assess how they will behave in a cloud environment. This complexity can also make it challenging to migrate data and workloads effectively.
- Costs: Migration can save organizational costs overall, but organizations need to carefully consider whether the benefits of migration justify the costs.
- Risk: Migrating mission-critical applications to the cloud carries risks, such as data loss or downtime during migration. Organizations need to carefully assess these risks before going ahead with migration.
What are a few key considerations to look for when moving your workloads to cloud?
To identify the cloud migration roadmap for desired outcomes, businesses must strategize and follow certain principles:
- Business and IT consultation: Assessing the current business IT infrastructure and recommending optimizing it for greater efficiency and cost savings. Get advice on how to adopt the cloud migration process and align IT with the overall business strategy.
- Business case validation: Evaluating the success of a business case in terms of return on investment, financial feasibility, market opportunity, operational feasibility, and other factors that may impact the success. Business case validation helps businesses make informed decisions about whether to pursue the process or not.
- Assessment of cloud operation maturity: Identify the current operational maturity of cloud operations and get recommendations on how to improve the cloud operations of an organization in terms of cloud governance, architecture, security, processes, and monitoring.
- Assessment of the application architecture and existing setup: Procedure a thorough review of structure, components, and processes that make up the application. Analyze the system architecture and its design, data flows, security, and assess the existing application’s performance, scalability, and reliability. By understanding the current architecture and setup, the team can develop strategies for improvement.
- Compliance with regulations and policies: It is important to be aware of regulations that apply to the business and to ensure that it complies with all of them. These policies should be updated regularly to reflect any changes to the regulations. Therefore, stay up to date on the changes to remain compliant.
- Analyzing migration options and identifying potential risks: After analyzing the various migration options available, it is important to identify the potential risks. These risks may include technical incompatibility, cost and time overruns, and a lack of resources or expertise.
- Optimization opportunities for capacity and cost: Companies should look at their current processes and identify areas that can be improved to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Analyzing the resources being used and evaluating if there are opportunities for cost savings or increased efficiency. Technology can be used to automate specific processes and reduce manual costs.
- Roadmap to target state: Evaluating the current state, developing a strategy for improvement, and implementing the necessary changes. The roadmap should identify potential risks and include a plan for mitigating them to ensure a successful transition to the target state. Once the roadmap is complete, it should be monitored and revised as necessary to ensure the target state is achieved.
Cloud Migration Types:
- Migrate and Modernize
- Cloud Infrastructure Ready Applications: These are IaaS applications, no need for code changes where you need to migrate ready applications to the cloud just lift and shift.
- Cloud Optimized Applications: These applications are containerized, and PaaS based applications where minimal code changes are needed.
- Cloud-native Applications: Applications are developed to reside in the cloud from start. Applications are modernized or rewritten and developed on the technologies of microservices architecture & serverless.
- Innovation: Innovate applications and develop new digital products for enterprise-specific needs and noncommercial needs. Examples are CRM and ERP, interacting with devices such as IoT, IoE, gaming applications, AR & VR applications, and Data Analytics.
Cloud Migration Strategies:
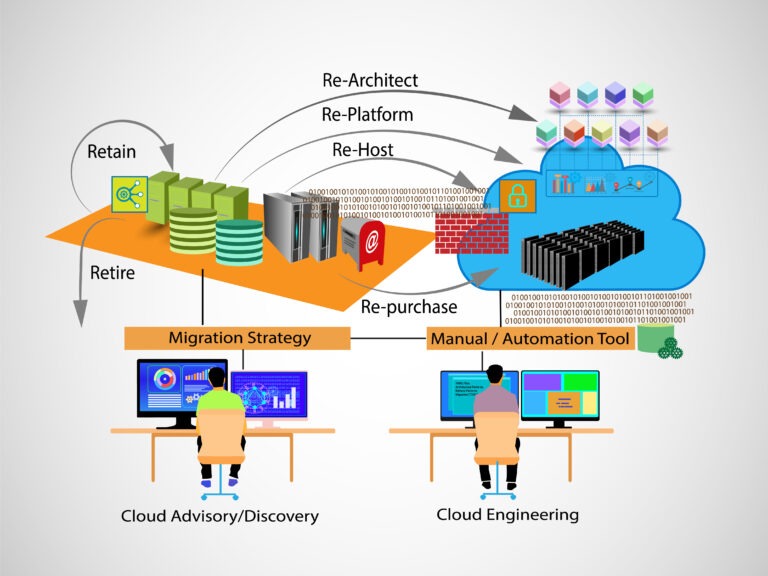
A cloud migration strategy is the process of moving workloads and applications from on-premises or legacy systems to cloud environments such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure. Cloud migrations are complex projects that require careful planning and execution. Therefore, enterprises need to understand their existing infrastructure, workloads and applications, security needs, deployment models, cost optimization strategies, disaster recovery plans, and other considerations when migrating.
- Retain is used to place an existing application or system running in its current form without any change. when an organization decides to keep existing systems and processes in place despite being available in the cloud. The primary benefit of this approach is that organizations can understand the costs associated with cloud services before committing to full cloud migrations.
- Rehost (lift and shift) is the process of moving an existing application or workload onto cloud infrastructure without any modifications, often referred to as “lift and shift”. This is the quickest approach for cloud migration as it requires minimal effort on the part of the IT (Information Technology) team. Example: Migrating on-premises Oracle database to EC2 instance in AWS cloud.
- Rebuild/Replatform (lift and reshape) refers to redeveloping existing applications from scratch with cloud-native components. This approach allows for greater scalability and flexibility, but usually requires a significant investment in terms of time and resources. Example: Migrating on-premises Oracle database to a Relational Database.
- Retire means retiring any existing service or application that has reached the end of its life cycle and is no longer in active use by the organization. As cloud computing becomes increasingly available and reliable, organizations should consider migrating from outdated services and applications as part of their cloud migration strategy.
- Refactor/rearchitect involves modifying existing cloud applications to improve their performance and scalability. This may involve rewriting code, changing database structures, introducing cloud services such as storage and caching, or reconfiguring application architecture. In simple, moving an application and modifying its architecture. Example: Migrating on-premises Oracle database to PostgreSQL a compatible edition.
- Repurchase/Replace (drop and shop) is when cloud-native solutions are purchased instead of migrating existing applications. It involves selecting appropriate products that can meet the needs of an organization and ensuring they are compatible with cloud hardware. Example: Migrating CRM system to salesforce or other CRM product.
- Relocate (Hypervisor level lift and shift) Cloud migration without modifying existing operations, rewriting software, or purchasing new hardware. Example: Relocating an Oracle database to VMware Cloud on Amazon Web Services.
Benefits of cloud migration
There are many reasons why companies are choosing to migrate to cloud including:
- Increased scalability: Businesses can scale up or down as needed, without having to make a major investment in new infrastructure.
- Improved flexibility: Cloud-based solutions offer greater flexibility than on-premises systems, making it easier for businesses to adapt their IT infrastructure to changing needs.
- Reduced costs: Help businesses reduce IT costs so businesses can eliminate the need for expensive on-premises hardware and software licenses.
- Increased productivity: Cloud migration can also lead to increased productivity, as employees can access cloud-based applications and data from anywhere, at any time.
- Improved disaster recovery: With cloud backup and disaster recovery solutions, businesses can ensure that their critical data is always safe and accessible, even in case of a major outage or disaster.
- Enhanced security: Businesses can take advantage of enhanced security features and protocols that are often not available with on-premises systems.
“To ensure your cloud migration goes smoothly, work with a professional cloud service provider.“
With a comprehensive approach to the process, firms can avoid disruption of services and maximize the business benefits offered by modern cloud-native apps. With careful planning and consideration of all aspects of the project, companies should be able to leverage the advantages that migrating their workloads offers them.